CNC turning services have become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility. This article delves into the various aspects that make CNC turning services stand out, exploring their processes, advantages, applications, and the technology behind them.
Understanding CNC Turning
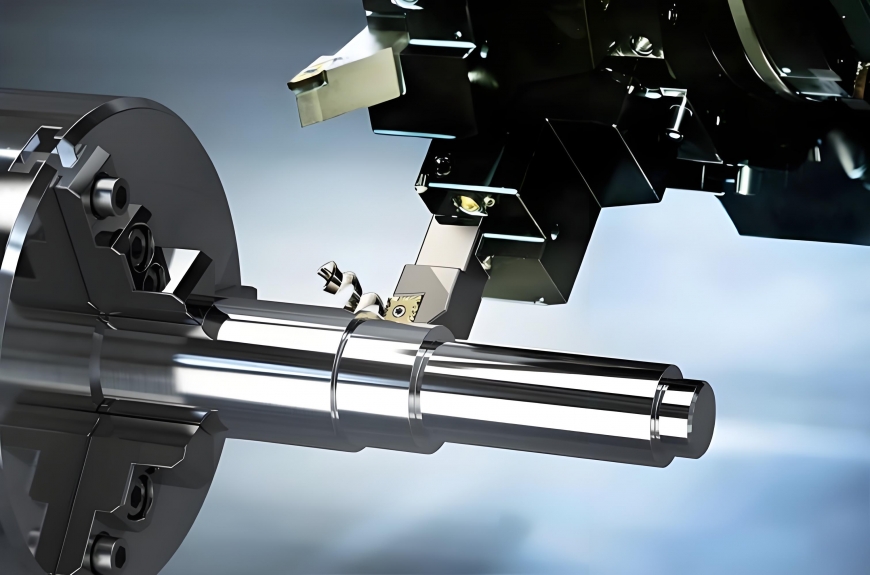
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning is a subtractive manufacturing process that involves rotating a workpiece while a cutting tool removes material to create the desired shape. This process is essential for producing cylindrical parts with high precision and repeatability. The ability to control the movement of the cutting tool with computer software allows for intricate designs and complex geometries that would be challenging to achieve with manual machining.
The CNC Turning Process
The CNC turning process begins with a raw material, typically in the form of a cylindrical bar. The material is secured in a lathe, which rotates it at high speeds. A cutting tool, controlled by a computer program, moves along the surface of the rotating workpiece, removing material to achieve the desired dimensions. This process can create various features, including grooves, threads, and complex shapes. The precision of CNC turning allows for the production of parts that not only meet but often exceed industry standards, making it a preferred choice for high-stakes applications.
Key Components of CNC Turning
CNC Lathe: The primary machine used in CNC turning, equipped with a rotating spindle and a cutting tool. Modern CNC lathes come with advanced features such as live tooling, which allows for additional operations like drilling and milling without changing the setup.
Control Software: The software that dictates the movements of the cutting tool based on pre-programmed designs. This software often includes simulation capabilities, allowing manufacturers to visualize the machining process before actual production, reducing errors and material waste.
Cutting Tools: Specialized tools designed for specific materials and shapes, ensuring efficient material removal. The choice of cutting tool can significantly impact the quality of the finished product, with advancements in tool materials and coatings enhancing performance and longevity.
Advantages of CNC Turning Services
CNC turning services offer numerous advantages that make them a preferred choice in manufacturing.
High Precision and Accuracy
One of the standout features of CNC turning is its ability to achieve tight tolerances, often within ±0.01 mm. This level of precision is crucial for applications where exact dimensions are necessary, such as in the aerospace and medical industries. The accuracy of CNC turning not only ensures that parts fit together correctly but also enhances the overall performance and reliability of the final product.
Efficiency and Speed
CNC turning is known for its rapid production capabilities. The automated nature of CNC machines allows for continuous operation, significantly reducing production times compared to manual machining. This efficiency is particularly beneficial for high-volume production runs, where the ability to produce large quantities of parts quickly can lead to substantial cost savings and improved turnaround times for customers.
Versatility in Design
CNC turning can accommodate a wide range of designs and materials. Whether producing simple shafts or complex components with intricate features, CNC turning can adapt to various manufacturing needs. This versatility makes it suitable for industries ranging from automotive to electronics, allowing manufacturers to respond quickly to changing market demands and customer specifications.
Consistency and Repeatability
Once a CNC program is established, the machine can produce identical parts with consistent quality. This repeatability is essential for manufacturers who require large quantities of the same component without variations in quality. The ability to maintain high standards across production runs not only enhances customer satisfaction but also builds trust in the manufacturer's capabilities.
Applications of CNC Turning
CNC turning services are utilized across various industries, each benefiting from the precision and efficiency of this manufacturing process.
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, components must meet stringent safety and performance standards. CNC turning is used to manufacture parts such as turbine blades, landing gear components, and structural elements, ensuring they meet the required specifications. The high precision of CNC turning is critical in this industry, where even the smallest deviation can have significant consequences for safety and performance.
Medical Devices
The medical industry relies on CNC turning for producing high-precision components used in surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. The ability to create complex geometries with tight tolerances is critical in this field. Additionally, the materials used in medical devices often require special considerations, such as biocompatibility, which CNC turning can accommodate through careful material selection and processing techniques.
Automotive Manufacturing
CNC turning plays a vital role in automotive manufacturing, producing parts like engine components, transmission housings, and various fittings. The efficiency and precision of CNC turning help manufacturers meet the high demands of the automotive market. As the industry moves towards more electric and hybrid vehicles, CNC turning will continue to evolve, producing components that support new technologies and designs.
Electronics
In electronics, CNC turning is used to create components such as connectors, housings, and heat sinks. The ability to work with small, intricate parts makes CNC turning ideal for this industry. As electronic devices become more compact and complex, the demand for precision-engineered components will only increase, further solidifying the role of CNC turning in electronics manufacturing.
The Technology Behind CNC Turning
The technology that powers CNC turning services has evolved significantly, enhancing their capabilities and efficiency.
Advanced CNC Software
Modern CNC machines are equipped with sophisticated software that allows for complex programming and simulation. This software enables manufacturers to visualize the machining process, optimize tool paths, and reduce material waste. The integration of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software streamlines the design-to-production workflow, allowing for faster prototyping and production cycles.
Tooling Innovations
Advancements in cutting tool technology have improved the efficiency and effectiveness of CNC turning. High-speed steel, carbide, and ceramic tools are designed to withstand the rigors of machining while providing superior cutting performance. Innovations such as coated tools enhance durability and reduce friction, allowing for faster cutting speeds and improved surface finishes.

Automation and Robotics
The integration of automation and robotics in CNC turning has further enhanced production capabilities. Automated loading and unloading systems, along with robotic arms, streamline the manufacturing process, reducing labor costs and increasing output. This automation not only improves efficiency but also minimizes the risk of human error, leading to higher quality products.
Challenges in CNC Turning
While CNC turning offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges.
Initial Setup Costs
The initial investment in CNC machinery and software can be significant. However, this cost is often offset by the long-term savings achieved through increased efficiency and reduced labor costs. Manufacturers must carefully evaluate their production needs and potential return on investment when considering CNC turning services.
Skill Requirements
Operating CNC machines requires skilled personnel who understand both the technology and the intricacies of machining. Training and retaining qualified operators can be a challenge for manufacturers. As technology continues to advance, ongoing education and training will be essential to keep staff updated on the latest techniques and best practices.
Material Limitations
Certain materials may pose challenges in CNC turning due to their hardness or brittleness. Manufacturers must carefully select materials that are compatible with the CNC turning process to ensure optimal results. Additionally, the choice of material can impact tool wear and machining efficiency, necessitating a thorough understanding of material properties.
Future Trends in CNC Turning
As technology continues to advance, the future of CNC turning services looks promising.
Increased Automation
The trend towards greater automation in manufacturing is expected to continue, with more CNC machines incorporating advanced robotics and AI-driven systems. This will enhance efficiency and reduce the need for manual intervention. As manufacturers seek to optimize production processes, the integration of smart technologies will play a crucial role in achieving higher levels of productivity.
Sustainable Manufacturing
With a growing emphasis on sustainability, CNC turning services are likely to adopt more eco-friendly practices. This includes optimizing material usage, reducing waste, and utilizing sustainable materials. Manufacturers are increasingly aware of their environmental impact and are seeking ways to minimize it while maintaining high-quality production standards.
Integration with Additive Manufacturing
The combination of CNC turning with additive manufacturing techniques is gaining traction. This hybrid approach allows for the creation of complex parts that may be difficult to achieve with traditional methods alone. By leveraging the strengths of both CNC turning and additive manufacturing, manufacturers can produce innovative designs that meet the demands of modern applications.

Conclusion
CNC turning services stand out in the manufacturing landscape due to their precision, efficiency, and versatility. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality, reliable CNC turning will only increase. By embracing technological advancements and addressing the challenges associated with CNC turning, manufacturers can position themselves for success in a competitive market.
Frequently Asked Questions regarding CNC Turning Service
1. What materials can be used in CNC turning?
CNC turning can accommodate a wide range of materials, including metals such as aluminum, steel, brass, and titanium, as well as plastics and composites. The choice of material often depends on the specific application and the required properties of the finished part.
2. How does CNC turning differ from CNC milling?
CNC turning involves rotating the workpiece while a stationary cutting tool removes material, primarily used for cylindrical parts. In contrast, CNC milling involves moving the cutting tool across the stationary workpiece, allowing for the creation of flat surfaces, complex shapes, and features like pockets and slots.
3. What industries benefit most from CNC turning services?
CNC turning services are widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, electronics, and manufacturing. Each of these sectors requires high precision and efficiency, making CNC turning an ideal choice for producing critical components.
4. What are the typical tolerances achievable with CNC turning?
CNC turning can achieve tight tolerances, often within ±0.01 mm. The exact tolerance depends on factors such as the material being machined, the complexity of the part, and the capabilities of the CNC machine being used.
5. How can manufacturers ensure the quality of CNC-turned parts?
Manufacturers can ensure the quality of CNC-turned parts by implementing rigorous quality control measures, including regular calibration of CNC machines, using high-quality cutting tools, and conducting inspections throughout the production process. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) can also help monitor and maintain quality standards.






