please click here:
https://www.sscontrolline.com/welded-coiled-tubing.html
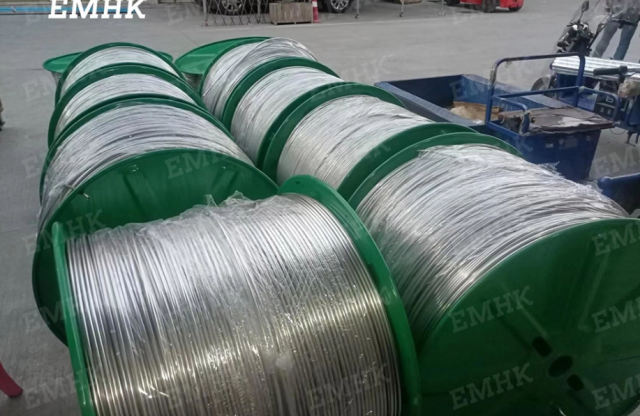
Introduction to Welded Coiled Tubing
Coiled tubing (CT) has revolutionized operations in the oil and gas industry, offering a flexible and efficient alternative to traditional jointed pipe for various well interventions and drilling activities. Welded coiled tubing, specifically, plays a crucial role due to its manufacturing process, which allows for long, continuous lengths essential for deep-well applications. This article delves into the intricacies of welded coiled tubing manufacturing, exploring the methods, materials, applications, and future trends shaping this critical sector.
Manufacturing Processes of Welded Coiled Tubing
The manufacturing of welded coiled tubing involves several sophisticated processes, each contributing to the final product's integrity and performance.
Material Selection and Preparation
The choice of material is paramount, with carbon steel being a common option due to its balance of strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels and stainless steel are also used for enhanced corrosion resistance and durability in harsh environments. The selected material must undergo rigorous testing to ensure it meets the required specifications for chemical composition and mechanical properties.
Strip Joining and Welding
The initial step involves joining multiple strips of the chosen material to achieve the desired length of the coiled tubing. Traditionally, these strips are joined using welding processes such as Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG), Metal Active Gas (MAG), or plasma welding. However, friction stir welding (FSW) is emerging as a superior alternative, offering several advantages:
-
Elimination of edge defects.
-
No need for filler metal, ensuring consistent material properties across the weld.
-
Reduced risk of cracking and corrosion.
Continuous Tube Forming
After the strips are joined, they are fed into a tube mill, where a series of rollers gradually form the flat strip into a tubular shape. High-frequency induction welding (HFIW) is then employed to weld the edges of the tube together, creating a continuous, joint-free pipe. The welding process parameters, such as current, voltage, and frequency, are carefully controlled to ensure a high-quality weld.
Quality Control and Testing
Stringent quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to detect any defects and ensure the coiled tubing meets the required standards. Non-destructive testing methods, such as eddy current testing (ECT) and ultrasonic testing (UT), are used to inspect the weld seam and base material for any imperfections. Mechanical testing, including tensile, hardness, and flattening tests, is also performed to verify the mechanical properties of the coiled tubing.
Coiling and Spooling
The final step involves coiling the continuous tube onto a spool for transportation and deployment. The coiling process must be carefully controlled to avoid damaging the tube or introducing residual stresses.
Key Technologies in Coiled Tubing Manufacturing
Several key technologies contribute to the production of high-quality welded coiled tubing.
Friction Stir Welding (FSW)
FSW is a solid-state welding process that joins materials without melting them. A rotating tool is inserted into the joint between two metal sheets, and the friction generates heat that softens the material, allowing it to be stirred and forged together. FSW offers several advantages over traditional welding methods, including:
-
Superior weld quality with minimal defects.
-
Improved mechanical properties.
-
Reduced distortion and residual stresses.
-
Environmentally friendly process with no fumes or spatter.
High-Frequency Induction Welding (HFIW)
HFIW is a welding process that uses high-frequency electromagnetic induction to heat the edges of the tube to be joined12. Once the edges reach the welding temperature, they are pressed together to form a continuous weld12. HFIW is a fast and efficient welding method that is well-suited for producing long lengths of coiled tubing12.
Controlled Rolling and Cooling
Controlled rolling and cooling are critical processes for achieving the desired microstructure and mechanical properties in the steel. By carefully controlling the temperature and deformation during rolling, the grain size and phase distribution of the steel can be optimized. Subsequent controlled cooling further refines the microstructure and enhances the strength and toughness of the coiled tubing.
Applications of Welded Coiled Tubing
Welded coiled tubing finds extensive applications across various industries, with a primary focus on oil and gas operations.
Oil and Gas Industry
-
Well Intervention: CT is used for wellbore cleaning, scale removal, and maintenance, ensuring optimal production.
-
Drilling: CT drilling offers a more efficient method for shallow and deep wells.
-
Hydraulic Fracturing: CT accurately delivers fracturing fluids to enhance production.
-
Fishing Operations: CT retrieves lost tools or equipment from wells.
Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
-
Fluid Injection: CT ensures the precise injection of chemicals into reactors and pipelines.
-
Maintenance: CT cleans pipelines and performs chemical treatments to maintain efficiency.
Other Industries
-
Heat Exchange Systems: CT is used in HVAC systems and cooling towers for efficient heat transfer.
-
Water Treatment: CT is utilized in distribution systems to ensure continuous flow and minimize leakage risks.
Advantages of Using Welded Coiled Tubing
Welded coiled tubing offers numerous advantages over traditional jointed pipes, making it a preferred choice for many applications.
Cost Efficiency
CT operations often require fewer personnel and less equipment, reducing manpower and mobilization costs.
Time Savings
CT operations are faster, allowing for continuous operations without frequent interruptions.
Reduced Environmental Impact
CT operations have smaller footprints and produce less waste, minimizing environmental impact.
Enhanced Safety
Fewer manual handling requirements and reduced rig-up time enhance safety for on-site personnel.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite its advantages, welded coiled tubing faces certain challenges that the industry is actively addressing.
Fatigue Life
The repeated bending and flexing of coiled tubing during operations can lead to fatigue damage and potential failure. Researchers are exploring new materials and manufacturing processes to improve the fatigue resistance of coiled tubing.
Corrosion Resistance
The harsh environments in which coiled tubing is used can cause corrosion, which can compromise its integrity. Ongoing efforts are focused on developing corrosion-resistant alloys and coatings to extend the service life of coiled tubing.
Advancements in Welding Techniques
Continued research and development in welding technologies, such as friction stir welding, are expected to further improve the quality and reliability of welded coiled tubing.
Automation and Robotics
The integration of automation and robotics in the manufacturing process can improve efficiency, reduce human error, and enhance safety.
Conclusion
Welded coiled tubing is a critical component in the oil and gas industry, enabling efficient and cost-effective well interventions and drilling operations. Ongoing advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and welding techniques are continuously improving the performance and reliability of coiled tubing, ensuring its continued importance in the future. As the industry continues to push the boundaries of deep-well exploration and production, welded coiled tubing will play an increasingly vital role in unlocking new resources and optimizing existing operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the typical length of a coiled tubing string?
-
Coiled tubing strings can reach up to 20,000 feet (approximately 6,000 meters) or more, depending on the application and well depth.
-
-
What materials are commonly used in coiled tubing manufacturing?
-
Carbon steel, high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels, and stainless steel are commonly used, chosen for their strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance.
-
-
What is friction stir welding, and why is it beneficial in coiled tubing manufacturing?
-
Friction stir welding is a solid-state welding process that joins materials without melting them, resulting in superior weld quality, improved mechanical properties, and reduced residual stresses.
-
-
How is the quality of welded coiled tubing ensured during manufacturing?
-
Stringent quality control measures, including non-destructive testing methods like eddy current and ultrasonic testing, are implemented to detect defects and ensure the tubing meets required standards.
-
-
What are the primary applications of coiled tubing in the oil and gas industry?
-
Coiled tubing is used for well intervention, drilling, hydraulic fracturing, and fishing operations, among other applications.
-
Article Summary
This article provides an extensive overview of welded coiled tubing manufacturing, emphasizing its pivotal role in the oil and gas sector. It explores the detailed manufacturing processes, including material selection, welding techniques like friction stir welding, and stringent quality control measures. The article also highlights the various applications of coiled tubing, its advantages over traditional methods, and the ongoing challenges and future trends in the industry. The content underscores the importance of continuous innovation in materials and manufacturing processes to enhance the performance and reliability of coiled tubing in demanding operational environments.