Rapid prototyping is a transformative approach in product development that allows businesses to create and test prototypes quickly and efficiently. This method not only accelerates the development process but also enhances collaboration, reduces costs, and improves product quality. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of rapid prototyping services and how they can significantly impact product development.
Understanding Rapid Prototyping
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping refers to a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer-aided design (CAD) data. The primary goal is to visualize and test the design before full-scale production. This process can involve various technologies, including 3D printing, CNC machining, and injection molding. Each of these methods has its unique advantages and applications, allowing designers to choose the most suitable approach based on the specific requirements of their projects. The flexibility of rapid prototyping enables teams to explore multiple design iterations without the constraints of traditional manufacturing timelines.
The Importance of Rapid Prototyping in Product Development
In today's fast-paced market, the ability to bring products to market quickly is crucial. Rapid prototyping allows companies to:
Reduce Time-to-Market: By creating prototypes quickly, businesses can test and iterate designs faster, leading to shorter development cycles. This speed is essential in industries where consumer preferences change rapidly, and being first to market can provide a significant competitive advantage.
Enhance Collaboration: Prototypes facilitate better communication among team members, stakeholders, and potential users, ensuring that everyone is aligned on the product vision. This collaborative approach fosters innovation, as diverse perspectives can lead to more creative solutions and improvements.
Minimize Risks: Early testing of prototypes helps identify design flaws and usability issues before investing in full-scale production, reducing the risk of costly mistakes. By addressing potential problems early in the development process, companies can save time and resources, ultimately leading to a more successful product launch.
Key Benefits of Rapid Prototyping Services
Speed and Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of rapid prototyping is the speed at which prototypes can be produced. Traditional methods of product development can take months or even years, while rapid prototyping can reduce this time to weeks or even days. This efficiency allows companies to respond quickly to market demands and changes. The ability to rapidly iterate on designs means that teams can experiment with different features and functionalities, leading to more innovative products that better meet customer needs.
Cost-Effectiveness
Rapid prototyping can also be more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing methods. By identifying design flaws early in the process, companies can avoid the high costs associated with reworking or scrapping products that do not meet market needs. Additionally, the ability to produce small batches of prototypes means that companies can test multiple designs without committing to large production runs. This financial flexibility is particularly beneficial for startups and smaller companies that may have limited budgets for product development.
Improved Product Quality
With rapid prototyping, companies can conduct thorough testing and gather user feedback on prototypes before finalizing the design. This iterative process leads to improved product quality, as designers can make informed adjustments based on real-world testing and user input. The focus on user-centered design ensures that the final product not only meets technical specifications but also resonates with the target audience, enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
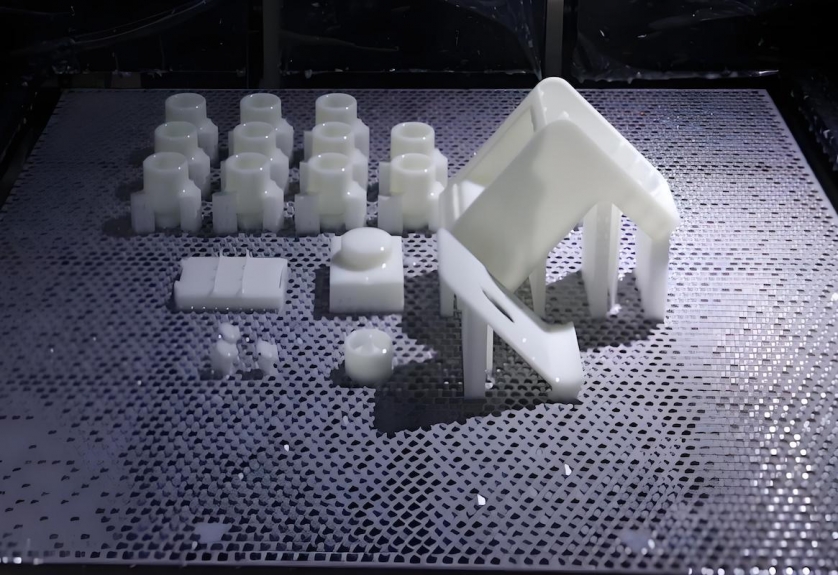

The Rapid Prototyping Process
Step 1: Ideation and Concept Development
The first step in the rapid prototyping process is ideation, where teams brainstorm and refine product concepts. This stage involves gathering input from various stakeholders, including designers, engineers, and potential users, to ensure that the product meets market needs. Effective ideation sessions can lead to innovative ideas that push the boundaries of what is possible, setting the stage for a successful product development journey.
Step 2: Creating the Prototype
Once the concept is finalized, the next step is to create the prototype. This can be done using various methods, such as 3D printing, which allows for quick and cost-effective production of complex designs. Other methods, like CNC machining, may be used for more precise and durable prototypes. The choice of prototyping method depends on factors such as the intended use of the prototype, the materials required, and the level of detail needed for testing.
Step 3: Testing and Feedback
After the prototype is created, it undergoes rigorous testing. This phase is crucial for identifying any design flaws or usability issues. Feedback is gathered from users and stakeholders, which informs necessary adjustments to the design. This step not only helps in refining the product but also builds a sense of ownership among team members and stakeholders, as they see their input directly influencing the development process.
Step 4: Iteration and Refinement
Based on the feedback received, the prototype is refined and iterated upon. This may involve multiple rounds of testing and adjustments until the product meets the desired specifications and user expectations. The iterative nature of rapid prototyping encourages a culture of continuous improvement, where teams are motivated to push the envelope and explore new possibilities.
Step 5: Finalization and Production
Once the prototype has been thoroughly tested and refined, the final design is prepared for production. Rapid prototyping allows for a smoother transition to full-scale manufacturing, as potential issues have already been addressed. This seamless handoff is critical for maintaining momentum and ensuring that the product launch is timely and successful.
Technologies Used in Rapid Prototyping
3D Printing
3D printing is one of the most popular methods of rapid prototyping. It allows for the creation of complex geometries and designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. Various materials can be used in 3D printing, including plastics, metals, and even ceramics. The versatility of 3D printing makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from consumer products to industrial components.
CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is another common method used in rapid prototyping. This technique involves using computer-controlled machines to cut and shape materials with high precision. CNC machining is ideal for creating functional prototypes that require durability and accuracy. The ability to work with a variety of materials, including metals and composites, makes CNC machining a valuable tool in the prototyping arsenal.
Injection Molding
While typically associated with mass production, injection molding can also be used in rapid prototyping. This method allows for the creation of high-quality plastic parts quickly and efficiently. It is particularly useful for testing the fit and function of components before full-scale production. The speed and efficiency of injection molding make it a popular choice for companies looking to validate their designs before committing to larger production runs.
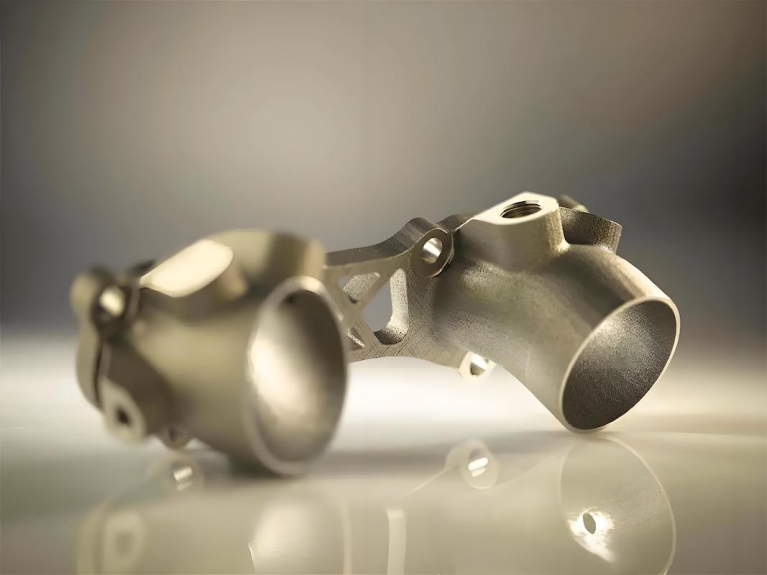

Applications of Rapid Prototyping
Consumer Products
Rapid prototyping is widely used in the development of consumer products, from electronics to household items. By quickly creating and testing prototypes, companies can ensure that their products meet consumer needs and preferences. This responsiveness to market trends is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the fast-evolving consumer landscape.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, rapid prototyping is used to develop new vehicle components and systems. This approach allows manufacturers to test designs for safety, performance, and aesthetics before committing to full-scale production. The ability to rapidly prototype parts can lead to significant improvements in vehicle design and functionality, ultimately enhancing the driving experience for consumers.
Medical Devices
The medical device industry benefits significantly from rapid prototyping. The ability to create and test prototypes quickly is essential for developing devices that meet stringent regulatory requirements and user needs. Rapid prototyping allows for the exploration of innovative solutions in medical technology, leading to advancements that can improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare processes.
Challenges in Rapid Prototyping
Material Limitations
While rapid prototyping offers many advantages, there are also challenges to consider. One of the primary limitations is the availability of materials. Not all materials are suitable for rapid prototyping, and some may not provide the necessary strength or durability for functional testing. As technology advances, however, new materials are continually being developed, expanding the possibilities for rapid prototyping applications.
Design Complexity
As designs become more complex, the rapid prototyping process can become more challenging. Ensuring that prototypes accurately represent the final product requires careful planning and execution. Designers must balance creativity with practicality, ensuring that innovative ideas can be effectively translated into functional prototypes.
Cost of Advanced Technologies
While rapid prototyping can be cost-effective, the initial investment in advanced technologies, such as 3D printers and CNC machines, can be significant. Companies must weigh the benefits against the costs to determine if rapid prototyping is the right approach for their needs. As the technology becomes more accessible and affordable, however, more businesses are likely to adopt rapid prototyping as a standard practice.
Future Trends in Rapid Prototyping
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The future of rapid prototyping is likely to see increased integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies can enhance the design process by providing insights and recommendations based on data analysis, leading to more efficient and effective prototyping. AI can also help in predicting potential design flaws, allowing teams to address issues proactively.
Sustainable Practices
As sustainability becomes a priority for many companies, rapid prototyping is evolving to incorporate more sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials and processes that minimize waste and energy consumption. The shift towards sustainability not only benefits the environment but also resonates with consumers who are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on a company's environmental impact.
Enhanced Collaboration Tools
The rise of remote work and global teams has led to the development of enhanced collaboration tools for rapid prototyping. These tools facilitate communication and feedback among team members, regardless of their location, ensuring that the prototyping process remains efficient and effective. By leveraging technology to improve collaboration, companies can harness the collective expertise of their teams, leading to better product outcomes.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping is a powerful tool that can significantly accelerate product development. By enabling quick iterations, enhancing collaboration, and improving product quality, rapid prototyping services are essential for businesses looking to thrive in today's competitive market. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for rapid prototyping to transform product development will only grow, making it an indispensable part of the innovation process. Embracing rapid prototyping not only streamlines the development process but also fosters a culture of innovation that can lead to groundbreaking products and solutions.

Frequently Asked Questions regarding Rapid Prototyping Service
1. What are the main advantages of using rapid prototyping in product development?
The main advantages include reduced time-to-market, cost-effectiveness, improved product quality, enhanced collaboration among team members, and the ability to minimize risks by identifying design flaws early in the process.
2. How does rapid prototyping differ from traditional prototyping methods?
Rapid prototyping focuses on quickly creating prototypes using advanced technologies like 3D printing and CNC machining, allowing for faster iterations and testing. Traditional methods often involve longer lead times and higher costs, making it less flexible in responding to design changes.
3. What industries benefit the most from rapid prototyping?
Industries that benefit significantly from rapid prototyping include consumer products, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. These sectors require quick iterations and testing to meet stringent market demands and regulatory standards.
4. What technologies are commonly used in rapid prototyping?
Common technologies include 3D printing, CNC machining, and injection molding. Each method has its unique advantages, such as the ability to create complex geometries with 3D printing or the precision of CNC machining.
5. What challenges might companies face when implementing rapid prototyping?
Companies may face challenges such as material limitations, design complexity, the initial cost of advanced technologies, and ensuring that prototypes accurately represent the final product. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and investment in the right tools and materials.






