In recent years, 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary technology in the manufacturing sector, enabling the production of customized products tailored to individual specifications. This article explores how customized manufacturing through 3D printing can meet unique needs across various industries, highlighting its benefits, applications, and future potential.
Understanding 3D Printing Technology
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects from a digital file. This technology builds objects layer by layer, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. The materials used in 3D printing can vary widely, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biological materials. This versatility in materials opens up a world of possibilities, enabling the creation of everything from simple prototypes to highly sophisticated components used in critical applications like aerospace and medical devices.
The Process of 3D Printing
The 3D printing process typically involves several key steps:
Design Creation: The first step is to create a digital model of the object using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model serves as the blueprint for the printing process. Designers can utilize advanced software tools to simulate the object's performance and make adjustments before printing, ensuring that the final product meets all specifications.
Slicing: The digital model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers using slicing software. This step converts the model into a format that the 3D printer can understand. The slicing process is crucial as it determines how the printer will construct each layer, affecting the overall quality and strength of the final product.
Printing: The 3D printer begins to create the object by depositing material layer by layer according to the sliced design. This process can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the complexity and size of the object. The precision of the printer allows for the creation of highly detailed features that would be impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Post-Processing: After printing, the object may require additional finishing processes, such as sanding, painting, or assembling multiple parts. Post-processing is essential for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of the printed object, ensuring it meets the desired standards for use.
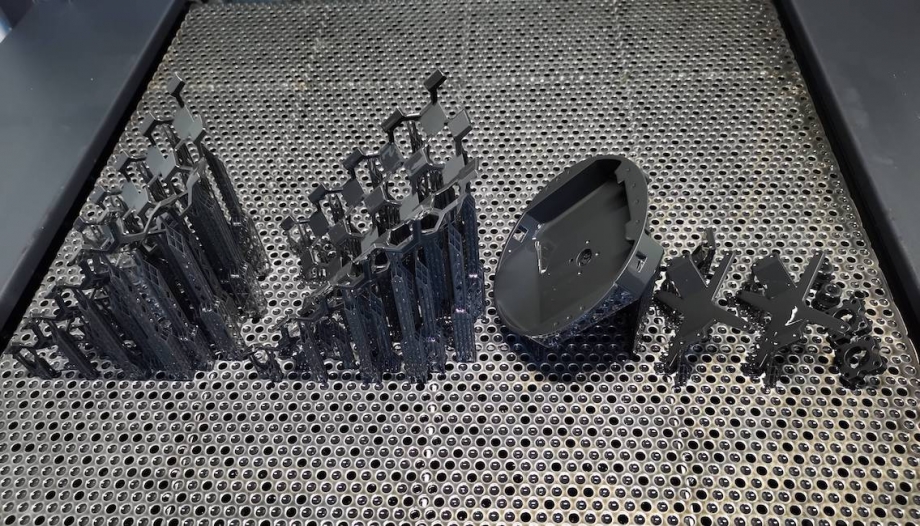
Benefits of Customized Manufacturing via 3D Printing
Flexibility and Design Freedom
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing is its flexibility. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that often require expensive molds and tooling, 3D printing allows for rapid design changes without incurring additional costs. This flexibility enables designers and engineers to experiment with new ideas and create unique products tailored to specific customer needs. The ability to quickly iterate on designs fosters innovation, allowing companies to respond swiftly to market demands and consumer preferences.
Cost-Effectiveness
Customized manufacturing through 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional methods, especially for small production runs. The elimination of tooling costs and the ability to produce items on demand reduces waste and lowers overall production costs. This is particularly beneficial for startups and small businesses looking to enter the market with unique products. Additionally, the reduced lead times associated with 3D printing mean that companies can bring their products to market faster, capturing opportunities before competitors.
Speed and Efficiency
3D printing significantly reduces the time required to bring a product from concept to market. Rapid prototyping allows for quick iterations and testing, enabling companies to refine their designs before full-scale production. This speed is crucial in industries where time-to-market can determine success. By streamlining the development process, businesses can not only save time but also allocate resources more effectively, focusing on innovation and customer engagement.
Sustainability
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, 3D printing offers a more environmentally friendly manufacturing option. The additive nature of 3D printing means that material is only used where necessary, reducing waste. Additionally, many 3D printing materials are recyclable or biodegradable, further minimizing the environmental impact. This focus on sustainability aligns with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, allowing companies to enhance their brand image while contributing to environmental conservation.
Applications of Customized 3D Printing
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, 3D printing is transforming the way medical devices and prosthetics are manufactured. Customized implants and prosthetics can be tailored to fit the unique anatomy of individual patients, improving comfort and functionality. Additionally, 3D printing is used to create surgical models that help surgeons plan complex procedures. This personalized approach not only enhances patient outcomes but also reduces the risk of complications during surgery, leading to better overall healthcare experiences.

Aerospace and Automotive
The aerospace and automotive industries are leveraging 3D printing to produce lightweight components that enhance fuel efficiency. Customized parts can be manufactured on demand, reducing inventory costs and lead times. Furthermore, the ability to create complex geometries allows for innovative designs that improve performance. In aerospace, for instance, 3D printing enables the production of intricate engine components that are both lighter and stronger, contributing to more efficient aircraft designs.
Fashion and Apparel
The fashion industry is embracing 3D printing to create unique clothing and accessories. Designers can produce custom-fit garments that cater to individual body shapes, reducing the need for alterations. This technology also enables the creation of intricate patterns and textures that would be difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. As a result, fashion brands can offer personalized products that resonate with consumers, fostering brand loyalty and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Consumer Goods
3D printing is revolutionizing the consumer goods market by allowing for mass customization. Products such as footwear, eyewear, and home decor can be tailored to meet individual preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction. This shift towards personalized products is changing the way consumers interact with brands. By offering customizable options, companies can create a more engaging shopping experience, encouraging consumers to express their individuality through their purchases.
Challenges and Considerations
Material Limitations
While 3D printing offers a wide range of materials, not all materials are suitable for every application. The properties of the material used can significantly impact the performance and durability of the final product. As technology advances, the development of new materials will expand the possibilities of 3D printing. Researchers are continually exploring innovative materials that can withstand extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive environments, broadening the scope of applications for 3D printing.
Regulatory Compliance
In industries such as healthcare and aerospace, products must meet strict regulatory standards. Ensuring that 3D printed products comply with these regulations can be challenging, particularly when it comes to safety and quality assurance. Manufacturers must invest in rigorous testing and certification processes to meet these requirements. This commitment to compliance not only protects consumers but also enhances the credibility of 3D printing as a reliable manufacturing method.

Intellectual Property Concerns
The ease of replicating designs through 3D printing raises concerns about intellectual property rights. As the technology becomes more accessible, protecting proprietary designs and innovations will be crucial for businesses. Companies must navigate the complexities of intellectual property law to safeguard their creations. This may involve implementing strategies such as digital rights management and secure file-sharing practices to prevent unauthorized reproduction of designs.
The Future of Customized Manufacturing via 3D Printing
Advancements in Technology
The future of 3D printing is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology. Innovations such as multi-material printing, improved printing speeds, and enhanced material properties will expand the capabilities of 3D printing. These advancements will enable even more complex and customized products to be manufactured. As research continues, we can expect to see breakthroughs that further enhance the precision and efficiency of 3D printing processes, making them even more viable for large-scale production.
Integration with Other Technologies
As 3D printing continues to evolve, its integration with other technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) will enhance its capabilities. AI can optimize design processes, while IoT can enable real-time monitoring of production, leading to greater efficiency and quality control. This convergence of technologies will create smart manufacturing environments where data-driven insights inform decision-making, ultimately improving product quality and operational efficiency.
Expanding Market Opportunities
The demand for customized products is expected to grow across various industries. As consumers increasingly seek personalized solutions, businesses that adopt 3D printing will be well-positioned to meet these needs. The ability to offer unique, tailored products will differentiate companies in a competitive market. Furthermore, as consumer preferences continue to evolve, businesses that embrace 3D printing will be better equipped to adapt to changing market dynamics and capitalize on emerging trends.
Conclusion
Customized manufacturing via 3D printing is revolutionizing the way products are designed and produced. With its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to meet unique needs, 3D printing is transforming industries from healthcare to fashion. As technology continues to advance, the potential for customized manufacturing will only expand, offering exciting opportunities for businesses and consumers alike. Embracing this innovative approach will be key to staying competitive in an ever-evolving market, paving the way for a future where personalized products are the norm rather than the exception.
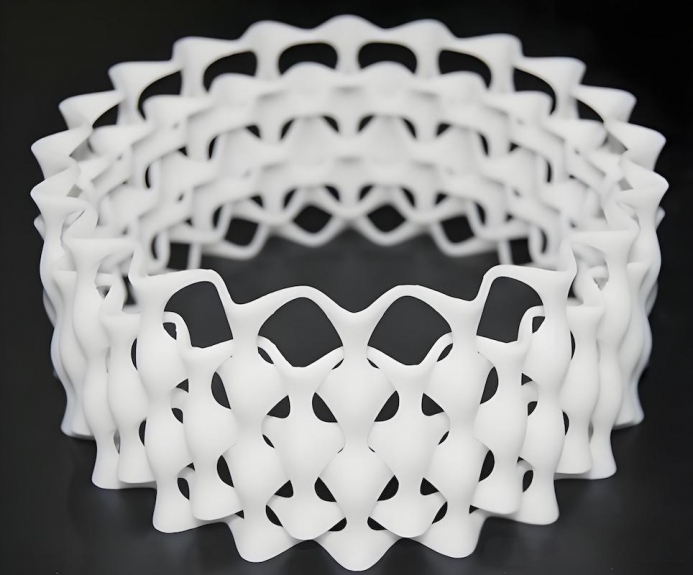
Frequently Asked Questions regarding 3D Printing
1. What industries benefit the most from 3D printing?
Industries such as healthcare, aerospace, automotive, fashion, and consumer goods benefit significantly from 3D printing. These sectors utilize the technology for rapid prototyping, customized products, and innovative designs that meet specific consumer needs.
2. How does 3D printing reduce production costs?
3D printing reduces production costs by eliminating the need for expensive molds and tooling, allowing for on-demand production. This minimizes waste and lowers inventory costs, making it particularly advantageous for small production runs and startups.
3. What are the environmental benefits of 3D printing?
3D printing is more environmentally friendly as it uses only the necessary material for production, reducing waste. Many 3D printing materials are recyclable or biodegradable, contributing to sustainability efforts in manufacturing.
4. Can 3D printing produce complex geometries?
Yes, 3D printing excels at producing complex geometries that are often impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability allows for innovative designs and intricate features that enhance product functionality and aesthetics.
5. What challenges do companies face when adopting 3D printing?
Companies face several challenges when adopting 3D printing, including material limitations, regulatory compliance, and intellectual property concerns. Ensuring product quality and safety while navigating these issues is crucial for successful implementation.





